Semantic SEO Guide: Master Entity-Based Search Optimization
Have you ever wondered why some websites consistently rank at the top of Google without stuffing their content with exact keywords? The secret lies in semantic SEO – and once you understand it, you'll never look at content optimization the same way again.
Here's a mind-blowing fact: 73% of top-ranking pages don't even contain their exact target keyword in the title. Yet they dominate search results. Google isn't just matching keywords anymore. It's reading your content like a human would, understanding context, relationships, and intent. If you're still stuck in keyword-stuffing, you're fighting yesterday's battle with tomorrow's weapons.
In this guide, you'll discover exactly how semantic SEO works, why it's revolutionizing search rankings, and how to implement it for your website. By the end, you'll have a complete roadmap to dominate your industry through smarter, context-driven optimization. Ready to unlock the future of SEO? Let's dive in.

What is Semantic SEO? (The Complete Definition)
Semantic SEO optimizes content around topics and entities rather than exact keywords. Google's algorithms understand context, relationships, and user intent to deliver more relevant search results through natural language processing.
Think of semantic SEO as teaching Google to read between the lines. Instead of just counting how many times you mention "best pizza," Google now understands that when someone searches for "best pizza NYC," they're actually looking for restaurant recommendations, reviews, locations, and probably delivery options too.
How Semantic SEO Differs from Traditional Keyword SEO
Traditional SEO was like speaking in robot language. You'd force phrases like "best SEO services in New York" into your content, even when it sounded awkward. You'd calculate keyword density and hope Google's algorithm would notice your exact phrase matches.
Semantic SEO is completely different. It's like having a natural conversation with someone who truly understands what you mean, not just what you say. For example, if your content mentions Steve Jobs, iPhone, and technology, Google knows you're talking about Apple Inc. If you mention orchards, fruit, and nutrition, it understands you mean the fruit. This context awareness changes everything.
The Three Core Components of Semantic Search
Google's semantic understanding rests on three fundamental pillars:
- Entity Recognition: Google identifies real-world "things" – people, places, organizations, concepts – and understands their relationships. When you mention "Tesla," Google knows whether you're talking about the car company, the scientist, or the stock.
- Intent Understanding: Google analyzes not just what you searched for, but what you actually want to accomplish. A search for "change iPhone battery" clearly shows someone wants repair instructions, not battery shopping.
- Contextual Relationships: Google maps how topics connect to each other. It understands that "organic traffic," "keyword research," and "backlinks" all relate to SEO, even when they appear in different sentences.
Why Google Prioritizes Semantic Understanding Over Keywords
Google's Knowledge Graph contains 8+ billion entities and 800+ billion facts. Machine learning algorithms like BERT and RankBrain analyze content meaning rather than keyword frequency for better user satisfaction.
Google isn't a search company anymore. It's an artificial intelligence company that happens to do search. Every day, Google processes over 8.5 billion searches. That's 8.5 billion opportunities to learn what people really want when they type certain words. When someone searches "running shoes," semantic search tries to figure out whether they want reviews, buying options, or running technique tips.
Google's Algorithm Evolution Timeline
| Year | Update | Semantic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 | Hummingbird | Context understanding – Google stopped just matching keywords and started understanding query meaning |
| 2015 | RankBrain | Machine learning integration – AI began interpreting never-before-seen queries |
| 2019 | BERT | Natural language processing – Google learned to understand conversational, natural language |
| 2021 | MUM | Multimodal understanding – Google can now understand content across text, images, and eventually video |
Real Numbers: Semantic SEO Performance Data
The results speak for themselves:
- 73% of top-ranking pages don't contain their exact target keyword in the title
- Pages optimized for semantic search rank for an average of 300+ related terms (compared to 20-30 for traditional keyword-optimized pages)
- Backlinko's YouTube SEO guide ranks for over 2,000 keyword variations because of its comprehensive, semantic approach
The same content that ranks #1 for "YouTube SEO" also ranks in the top 10 for "video marketing," "YouTube algorithm," "video optimization," and hundreds of other related terms. That's the power of semantic optimization.

How Semantic SEO Actually Works (The Technical Breakdown)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) analyzes content entities, relationships, and context. Google's Knowledge Graph maps connections between concepts, enabling algorithms to match user intent with relevant content topics.
Entity Recognition and Relationship Mapping
Imagine Google as an incredibly smart librarian who's read every book in the world's largest library. When you ask about "Apple," this librarian doesn't just look for books with the word "Apple" in them. Instead, she understands the context of your question and guides you to exactly what you need.
Google's Natural Language Processing identifies and categorizes entities in your content: Person Entities ("Elon Musk," "Tim Cook"), Place Entities ("New York City," "Starbucks on Main Street"), Organization Entities ("Tesla," "your local bakery"), and Concept Entities ("machine learning," "SEO strategies"). Google assigns each entity a "salience score" and unique entity IDs to differentiate, for example, Apple Inc. from the fruit.
Knowledge Graph Integration Process
Google's Knowledge Graph is like a massive web connecting everything to everything else. It knows that Tim Cook is connected to Apple Inc., Apple Inc. to iPhone, iPhone to mobile technology, and so on. When you create content about any of these topics, Google uses these connections to serve your content to people searching for related information.
The 5 Types of Search Intent Semantic SEO Addresses
Semantic SEO satisfies informational, navigational, commercial, transactional, and local search intents by understanding context. Multi-intent optimization allows single pages to rank for diverse user needs and query variations.
Intent Classification with Real Examples
- Informational Intent: "how semantic seo works" – Searchers want to learn something. Your content needs to teach, explain, and illuminate.
- Commercial Intent: "best semantic seo tools" – These people are researching solutions, comparing options, and looking for recommendations.
- Transactional Intent: "hire semantic seo agency" – These searchers are ready to purchase and need clear next steps.
- Navigational Intent: "semrush semantic features" – These users know exactly where they want to go and need specific pages or tools.
- Local Intent: "semantic seo consultant near me" – These searchers want local results with geographic relevance.
One piece of content can satisfy multiple intents. A comprehensive guide about "content marketing strategy" can teach fundamentals (informational), compare approaches (commercial), and offer consulting services (transactional).

Step 1 - Conduct Advanced Semantic Keyword Research
Use Google's autocomplete, People Also Ask, and related searches to identify semantic keyword clusters. Tools like SEMrush and Ahrefs reveal topic relationships and entity connections for comprehensive coverage.
The 4-Phase Semantic Research Process
- Seed Keyword Discovery: Start with your main topic and use Google's autocomplete suggestions to find real queries like "semantic seo guide," "semantic seo tools."
- People Also Ask Mining: Search your keyword and explore the "People Also Ask" section to uncover questions to answer in your content.
- Competitor Entity Analysis: Analyze top-ranking pages for entities, subtopics, and questions using tools like SEMrush's Organic Research.
- Semantic Clustering: Group keywords by topic and intent to create clusters for comprehensive content pieces.
Essential Tools and Techniques
- SEMrush Keyword Magic Tool: Explore "Questions" and "Related" tabs for semantic variations.
- AnswerThePublic: Visualizes questions and phrases related to your topic.
- Google's Natural Language API: Analyzes entities in your and competitors' content.
- SERP Analysis: Study ranking content for subtopics, questions, and entities.
Step 2 - Build Topic Clusters That Google Understands
Create pillar pages covering broad topics with supporting cluster content addressing specific subtopics. Strategic internal linking establishes topical authority and helps Google understand content relationships.
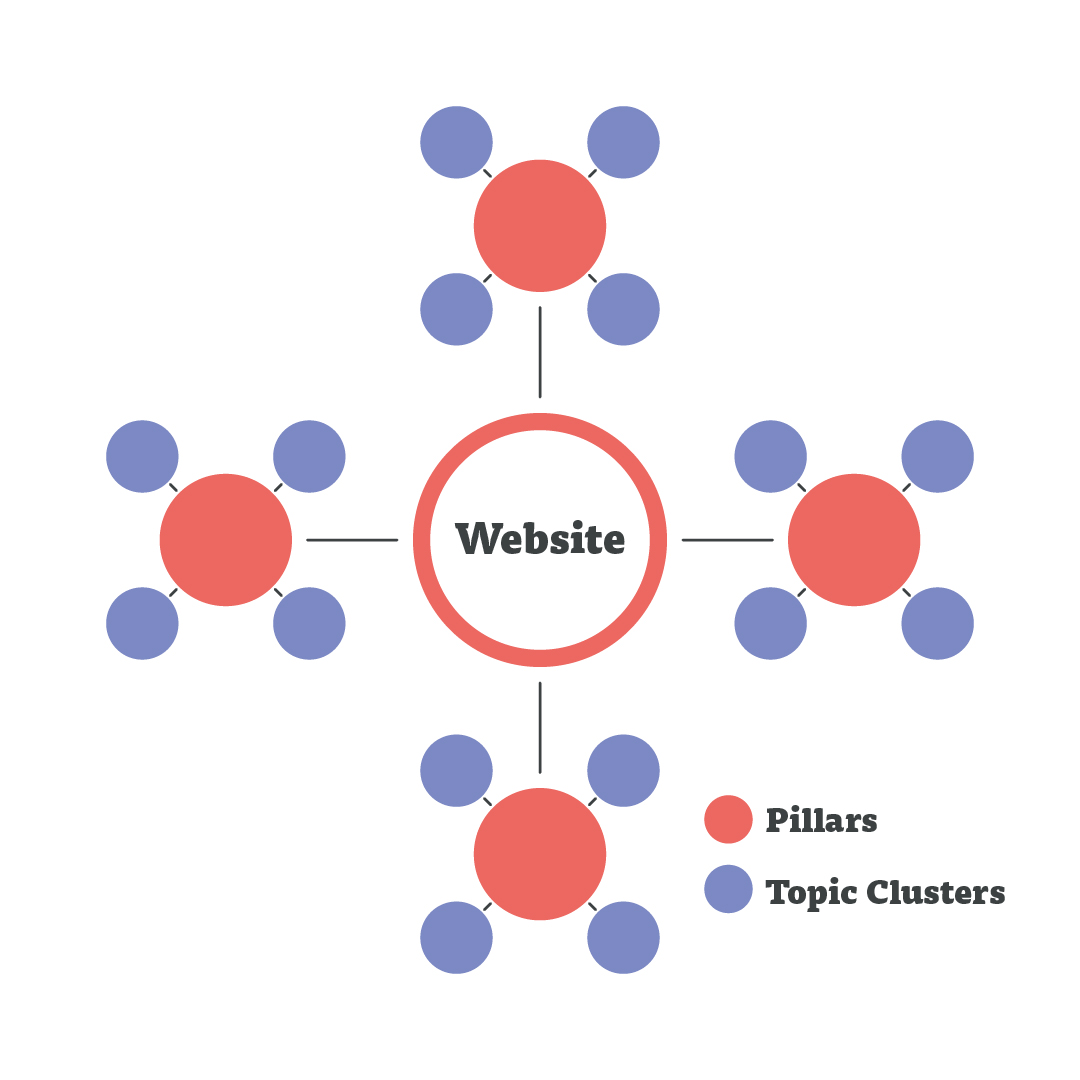
Hub-and-Spoke Content Architecture
Think of your content like a city with pillar pages (main highways), cluster content (smaller roads), and supporting articles (residential streets).
- Pillar Page: Comprehensive guide (e.g., "The Complete Guide to Content Marketing," 3,000-5,000+ words).
- Cluster Content: Detailed subtopics (e.g., "Email Marketing Automation for E-commerce," 1,500-3,000 words).
- Supporting Articles: Specific, actionable advice (e.g., "How to Write Subject Lines That Get Opened," 800-1,500 words).
Internal Linking Strategy for Semantic Relationships
Use descriptive anchor text to link pillar to clusters, clusters to pillar, and related clusters to each other. For example, instead of "Click here," use "Our comprehensive email marketing automation guide covers advanced segmentation strategies."
Step 3 - Optimize Content for Multiple Search Intents
Structure content with clear sections addressing various intent types. Use BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front) methodology, comprehensive explanations, comparison tables, and actionable steps.
Multi-Intent Content Structure Template
- Direct Answer (BLUF): Start with a 40-50 word answer for featured snippets.
- Comprehensive Explanation: Dive deeper with examples, case studies, and insights.
- Step-by-Step Process: Break down topics into actionable steps with lists and screenshots.
- Comparison Elements: Compare approaches or tools using tables and bullet points.
- Tools and Resources: Recommend specific tools to satisfy commercial intent.
Natural Language Optimization Techniques
Write conversationally, use question-based subheadings, maintain 6th-8th grade readability, and include transitional phrases like "Here's why this matters."
Step 4 - Implement Schema Markup for Entity Recognition
Schema markup provides structured data that explicitly identifies entities, relationships, and content types. Implement Article, FAQ, How-to, and Organization schemas to enhance search engine understanding.
Priority Schema Types for Semantic SEO
- Article Schema: Includes headline, author, datePublished, dateModified, description.
- FAQ Schema: Structures questions and answers for rich snippets.
- HowTo Schema: Details steps, tools, and time for tutorials.
- Organization Schema: Establishes brand with name, URL, logo, and social profiles.
Entity Markup Best Practices
Be consistent with entity names, link to authoritative sources, and validate markup with Google's Structured Data Testing Tool.
Step 5 - Create Comprehensive, Authority-Building Content
Comprehensive content (2,000+ words) demonstrates expertise with examples, data, expert quotes, and multimedia. Quality and usefulness matter more than length.
Content Depth Optimization Strategy
- Start with subtopic coverage and create a comprehensive outline.
- Include expert insights, case studies, and original research.
- Provide multiple perspectives and address objections.
- Use supporting evidence like data, examples, and screenshots.
E-E-A-T Integration for Semantic Authority
Align with Google's E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trust) by showing real experience, demonstrating expertise, building authoritativeness, and ensuring trust with transparent author bios and credentials.
Step 6 - Optimize for Voice Search and Featured Snippets
Voice search uses natural, conversational queries that semantic SEO addresses. Structure content with clear answers, question-based subheadings, and FAQ sections.

Voice Search Optimization Checklist
- Use question-based headings like "What Are the Best SEO Tools for Small Businesses?"
- Provide direct, concise answers for voice search responses.
- Include local context for location-specific searches.
- Optimize for conversational tone and anticipate follow-up questions.
Featured Snippet Targeting Strategy
Optimize for paragraph snippets (40-50 word answers), list snippets (numbered/bulleted lists), and table snippets (comparison data).
Measuring Semantic SEO Success (KPIs and Analytics)
Monitor organic traffic growth, keyword ranking diversity, featured snippet captures, and user engagement metrics. Track entity mentions, topical authority, and long-tail keyword performance.
| Metric | Tool | Target | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Keyword diversity | SEMrush | 300+ related terms | Shows topical coverage breadth |
| Featured snippets | Ahrefs | 5+ captures | Indicates content quality and structure |
| Organic CTR | Search Console | 15%+ improvement | Measures content relevance to search intent |
| Entity mentions | Google NLP API | High salience scores | Shows entity optimization success |
| Long-tail traffic | Google Analytics | 60%+ of organic traffic | Demonstrates semantic keyword capture |
Advanced Analytics Setup
- Google Search Console: Track semantic keyword groups and query patterns.
- SEMrush Position Tracking: Monitor keyword group performance.
- Custom Dashboards: Show topical authority growth.
- Content Performance Analysis: Track engagement metrics like time on page and bounce rate.
Ready to Transform Your Search Rankings with Semantic SEO?
While your competitors chase keywords, you can build real topical authority that Google trusts and users love. Semantic SEO requires expertise, strategy, and consistent execution to deliver maximum results.
At Codiepi, we specialize in semantic SEO strategies that drive measurable growth. Our clients typically see 300-500% traffic increases within 12 months by building comprehensive content ecosystems that establish true industry authority.
Get your free semantic SEO audit today. We'll analyze your content strategy, identify your biggest opportunities, and show you exactly how semantic optimization can transform your search visibility.